How to Choose a Power Supply
Choosing a good quality power supply for your build is key to making sure your system remains stable when it is working under any sort of load.
When you look at the listings for power supplies, you’ll see them range in output anywhere from 650W to 2000W. On some, you will also see an ’80 Plus’ certification and a rating anywhere from Bronze to Titanium. But what do those ratings mean, how will they affect you and how many watts do you need to power your PC?

Power Supply Form Factors
Power supplies come in different form factors designed to fit into different enclosures. For the vast majority of self-builders, the case you choose will determine the size of the power supply you need.
Your case specifications will tell you which power supply sizes it accepts. An ATX power supply will usually fit into a case that accepts an ATX motherboard, but one thing to look out for is that as power supply wattages increase, sometimes their physical depth can also increase. Widths and heights normally fit to a standard, but depths can vary.
A 500W ATX power supply could measure 150x86x160 mm, but a 1600W ATX power supply may measure 150x86x210 mm. Notice the 50mm increased depth on the higher wattage PSU? If you need a powerful PSU for your build because of a powerful CPU/GPU combo, take this into account, and make sure that your case will accommodate it. Most will, as there is usually plenty of room behind the PSU, but it is worth checking.
ATX power supplies have the greatest range available to the builder and are the most commonly used size. Many Micro or Mini ATX cases will usually give you enough space for an ATX power supply.
Here’s a list of common PSU sizes and their dimensions.
| PSU Size | Width (mm) | Height (mm) | Depth (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATX | 150 | 86 | 140 – 210 |
| TFX | 85 | 65 | 175 |
| SFX | 100 | 63.5 | 125 |
| SFX-L | 130 | 63.5 | 125 |
What is ATX 3.0 and do I need it?
ATX 3.0 is the first change in the ATX standard since 2003 and is driven by the power requirements of modern demanding GPUs. ATX 3.0 PSUs include a new GPU PCIe 5.0 12VHPWR 12+4 pin power connector that can supply from 150 to 600 watts directly to the GPU.
Current ATX GPU connections are 6 pin (75 watt) or 8 pin (150 watt) and high end GPUs often require several 6 or 8 pin connections to the PSU to enable drawing enough power.
ATX 3.0 will become the standard to support high end next generation GPUs, which will demand more power. Only current users of top end GPUs such as the RTX 4090, will see a benefit from this type of PSU. However, as a good quality PSU can last you through many computer upgrades, it’s worth thinking about purchasing the most recent standard upfront, even if you won’t immediately use it.
Do ATX 3.0 PSUs support older GPUs?
The ATX 3.0 standard means that PSUs adhering to this standard will come with a new 12+4 pin 12VHPWR connector. Current gen, and older generation GPUs require either 1 or 2 PCIe 6 or 8 pin connections.
There will be a long crossover period while older GPUs become obsolete, for this reason, most PSU manufacturers of modular power supplies offering the ATX 3.0 standard will still supply 6 and 8 pin PCIe connectors and connections for use with older GPUs.
What is a Modular Power Supply?
Modular power supplies are the most versatile kind. They allow you to only connect and power the devices you have within your system.
These power supplies come as a box with a series of sockets and a collection of cables. You simply connect only the sockets you need to the devices in your computer.
Using a modular power supply limits the amount of cables inside your build to only those necessary, and this helps make the inside of your case neater. They also allow for easy upgrades.
Non-modular power supplies are also available, but these come with a fixed number of pre-attached cables. If you don’t care about excess cabling inside your case, you may make a small saving by considering a non-modular power supply.
80 Plus Certification
80 Plus is a certification programme from https://www.clearesult.com/ that provides a way of easily identifying how efficient a power supply is. This scheme guarantees PSUs with the 80 Plus badge to be at least 80% efficient.
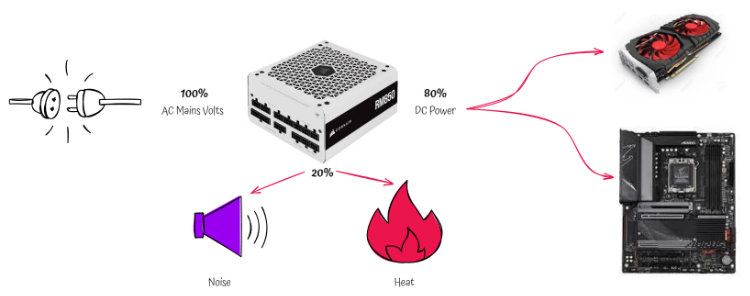
What is an 80% efficient CPU?
A computer power supply converts AC power from your wall socket into DC power for your computer parts. An 80% efficient PSU will ensure that 80% of the power taken from your wall socket gets converted into usable computer power. Excess heat and noise are where the remaining 20% usually go.
The higher the efficiency of your PSU, the less it will cost you to power your computer.
What are the 80 plus levels?
An 80 Plus badge certifies that a power supply is at least 80% efficient at 100% load, but the specification allows for more efficient power supplies to be given higher ratings as ’80 Plus Bronze’ through to ’80 Plus Titanium’ levels.
You can see from the table below that an 80 Plus Titanium PSU is actually at least 90% efficient in both Europe and anywhere else with a 115V mains power.
| Certification | 115V | 230V (EU) |
|---|---|---|
| 80 PLUS | 80% | 82% |
| 80 PLUS Bronze | 82% | 85% |
| 80 PLUS Silver | 85% | 87% |
| 80 PLUS Gold | 87% | 89% |
| 80 PLUS Platinum | 89% | 90% |
| 80 PLUS Titanium | 90% | 91% |
Will a Gold certified PSU last longer than a Bronze one?
80 Plus certification simply determines how efficient a power supply is. Usually, in order to gain more efficiency, manufacturers must use better quality, longer lasting components to build their device. However, this is not always true. Gold certification does not imply a Gold standard build or a Gold standard lifetime.
How Many Watts of Power Do I Need?
If you choose a power supply for your computer build that can’t supply enough watts, then your computer may boot and operate, but put it under any stress, its power requirements will increase and it will become unstable. This may lead to freezes, crashes or random resets. It’s critical that you ensure your supply has enough in the tank to always supply enough power.
Most computer components will give you some idea of how much power they consume at idle and under load. CPUs will list TDP figures in Watts. GPUs will also list this figure and because GPUs are often the most power hungry component of a system, they often also list a minimum system power requirement.
Nvidia GPU Power Requirements and Connectors
Here is a table of the last 2 generations of Nvidia GPU and their minimum recommended PSU requirements and PSU connections.
| GPU | Min Recommended PSU (W) | Required Connectors |
|---|---|---|
| RTX 4090 | 850 | 3x PCIe 8-pin cables (adapter in box) or 1x 450 W or greater PCIe Gen 5 cable. |
| RTX 4080 | 750 | 3x PCIe 8-pin cables (adapter in box) or 1x 450 W or greater PCIe Gen 5 cable. |
| RTX 4070 Ti | 700 | 2x PCIe 8-pin cables (adapter in box) or 300 W or greater PCIe Gen 5 cable. |
| RTX 4070 | 650 | 2x PCIe 8-pin cables (adapter in box) or 300 W or greater PCIe Gen 5 cable. Certain models may use 1x PCIe 8-pin cable. |
| RTX 4060 Ti | 550 | 1x PCIe 8-pin cables (adapter in box) or 300 W or greater PCIe Gen 5 cable. Certain models may use 1x PCIe 8-pin cable. |
| RTX 4060 | 550 | 1x PCIe 8-pin cables (adapter in box) or 300 W or greater PCIe Gen 5 cable. Certain models may use 1x PCIe 6-pin cable or 1x PCIe 8-pin cable. |
| RTX 3090 Ti | 850 | 3x PCIe 8-pin cables (adapter in box) OR 450W or greater PCIe Gen 5 cable |
| RTX 3090 | 750 | 2x PCIe 8-pin (adapter to 1x 12-pin included) |
| RTX 3080 Ti | 750 | 2x PCIe 8-pin (adapter to 1x 12-pin included) |
| RTX 3080 | 750 | 2x PCIe 8-pin (adapter to 1x 12-pin included) |
| RTX 3070 Ti | 750 | 2x PCIe 8-pin (adapter to 1x 12-pin included) |
| RTX 3070 | 650 | 1x PCIe 8-pin (adapter to 1x 12-pin included) |
| RTX 3060 Ti | 600 | 1x PCIe 8-pin (adapter to 1x 12-pin included) |
| RTX 3060 | 550 | 1x PCIe 8-pin |
| RTX 3050 | 550 | 1x PCIe 8-pin |
AMD GPU Power Requirements and Connectors
Here is a table of the last 2 generations of AMD GPU and their minimum recommended PSU requirements and PSU connections..
| GPU | Min Recommended PSU (W) | Required Connectors |
|---|---|---|
| RX 7900 XTX | 800 | 2x PCIe 8-pin cables |
| RX 7900 XT | 750 | 2x PCIe 8-pin cables |
| RX 7800 XT | 700 | 2x PCIe 8-pin cables |
| RX 7700 XT | 700 | 2x PCIe 8-pin cables |
| RX 7600 | 550 | 1x PCIe 8-pin cables |
| RX 6950 XT | 850 | 2x PCIe 8-pin cables |
| RX 6900 XT | 850 | 2x PCIe 8-pin cables |
| RX 6800 XT | 750 | 2x PCIe 8-pin cables |
| RX 6800 | 650 | 2x PCIe 8-pin cables |
| RX 6700 | 600 | 1x PCIe 8-pin cables |
Example PSU Requirement Calculation
When you know the TDP of your CPU and GPU, add them together, then because other components such as your motherboard, RAM and storage drives rarely list TDP figures, we need to estimate their usage.
| Component | Power Requirement | How to Find? |
|---|---|---|
| CPU (Intel Core i7-13700K) | 125 W | Product Specs |
| GPU (NVidia RTX 4060) | 115 W | Product Specs |
| RAM (64 GB DDR5) | 25 W | Estimate |
| Motherboard (ATX) | 70 W | Estimate |
| SSD Storage Drive (1TB) | 15 W | Estimate |
| HDD Storage Drive (1 TB, 10k RPM 3.5″) | 15 W | Estimate |
| Estimated Power Requirement | 365 W |
Once you have an estimated power requirement for your build, look for a PSU that more than meets these requirements. The more spare power you have, the more room you’ll have to upgrade components in the future.
Which PSU should I choose?
You should always choose a power supply from a well-known brand such as Corsair, Seasonic, Asus, Thermaltake, MSI, EVGA, Coolermaster, or Gigabyte (to name a few). It’s difficult to gauge power supplies based on customer reviews, because cheaply built ones will work, but who returns to a website after 2 years to say their cheap PSU failed?
A quality power supply from a reputable manufacturer can last you through many computer upgrades and live longer than many other components in your system. To gauge the minimum expected lifespan of a PSU is to look at the warranty offered by the manufacturer. A good warranty will be 10 years or more.
My general advice is to go with 80 Plus Silver or Gold level certification. If you live somewhere with high electricity costs and you use your computer regularly for work, it can be worth targeting a Platinum or even Titanium PSU, but the gains are marginal and price rises higher.